Back to article: Molecular targets of spermidine: implications for cancer suppression
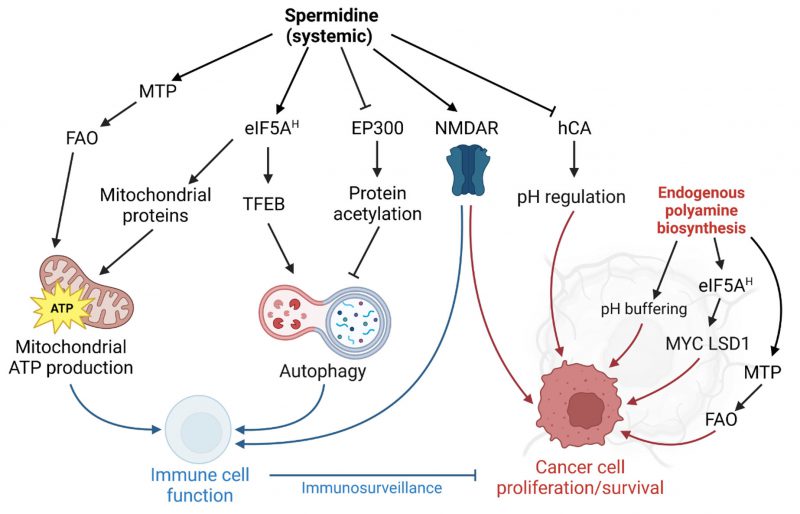
FIGURE 1: Model for spermidine-mediated effects in immune and cancer cells. Systemically supplied spermidine elicits antitumor responses predominantly through targeting pathways that improve immune cell function (blue arrows). However, in cancer cells or the tumor microenvironment regulation of these targets by endogenous polyamine biosynthesis may also promote proliferation and cancer cell survival (red arrows). See text for details. MTP, mitochondrial trifunctional protein. FAO, fatty acid oxidation. eIF5AH, hypusinated eukaryotic initiation factor 5A. TFEB, transcription factor EB. EP300, histone acetyltransferase E1A binding protein P300. NMDAR, N-methyl aspartate receptor. hCA, human carbonic anhydrase. LSD1, lysine-specific histone demethylase 1. ATP, adenosine triphosphate. Illustration generated with Biorender.