Back to article: VDAC1 at the crossroads of cell metabolism, apoptosis and cell stress
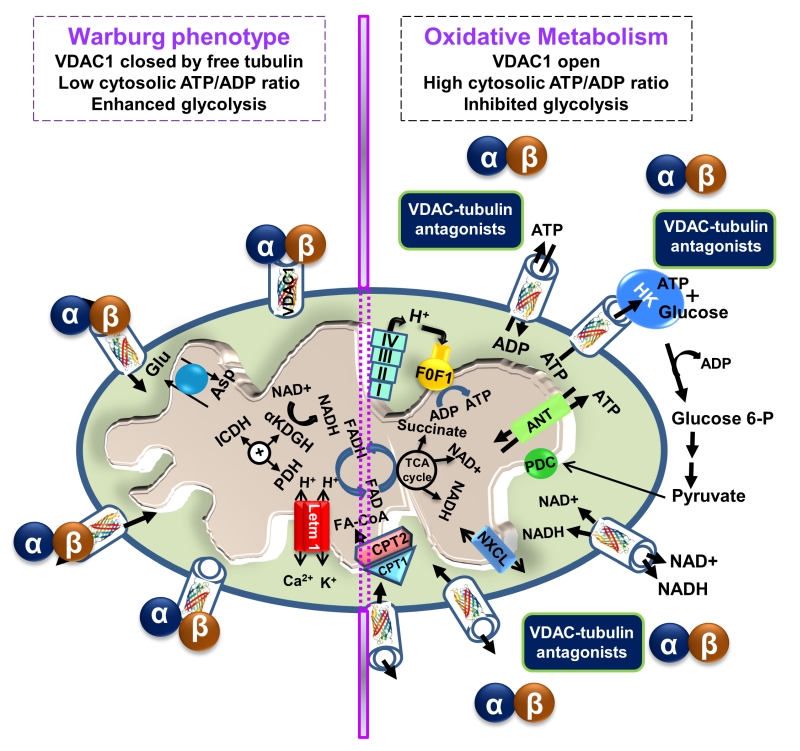
FIGURE 3: VDAC1-tubulin interaction: a metabolic switch to modulate mitochondrial metabolism in cancer cells. In cancer cells, high levels of free tubulin close VDAC1, decreasing the flux of metabolites, ATP and ADP through the OMM. VDAC1 closing leads to low generation of mitochondrial ATP and subsequently, to a low cytosolic ATP/ADP ratio that favors glycolysis in the Warburg phenotype. Erastin, a VDAC-tubulin antagonist, opens VDAC1 by blocking the inhibitory effect of free tubulin. VDAC1 opening leads to increased mitochondrial metabolism and to a high cytosolic ATP/ADP ratio that inhibits glycolysis and reverts the Warburg phenotype. αβ indicates tubulin heterodimers.