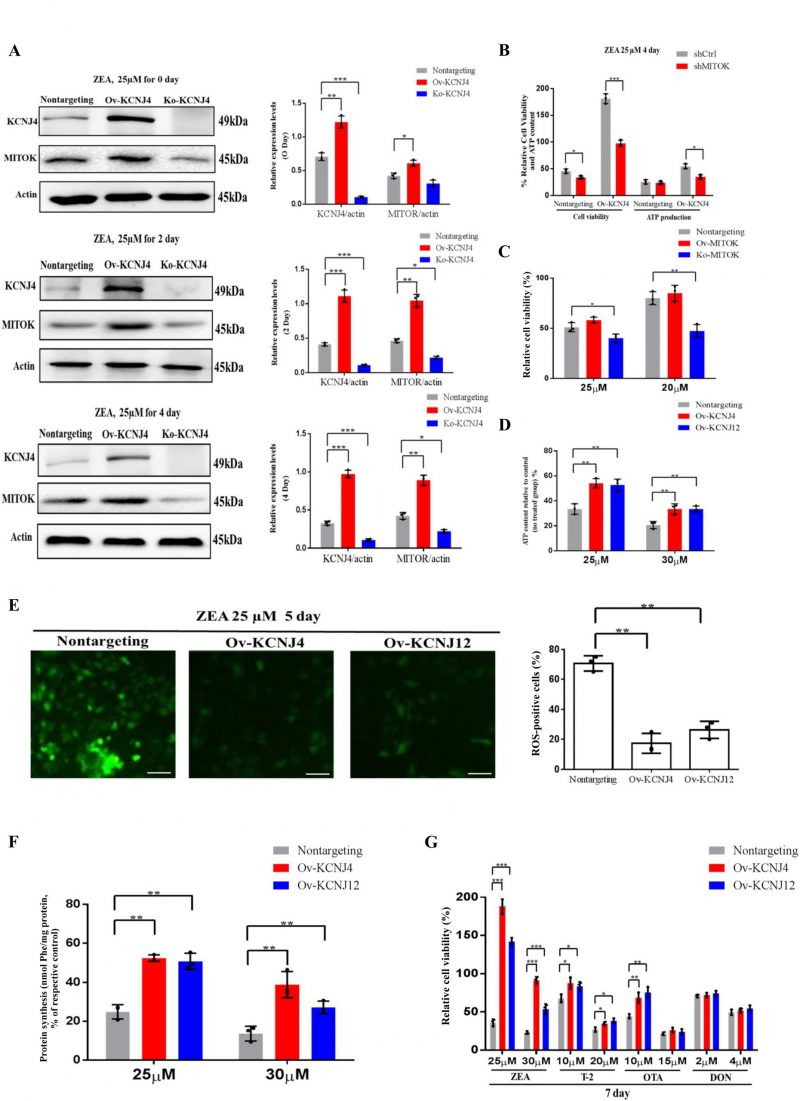
Back to article: CRISPR-activation screen identified potassium channels for protection against mycotoxins through cell cycle progression and mitochondrial function
FIGURE 4: High-level potassium channels cell lines attenuate the damage of cellular protein synthesis and mitochondrial under ZEA treatment. (A) Immunoblotting for KCNJ4, MITOK and actin expression after ZEA treatment in different times. (B) Effect of MITOK knockdown on cell viability and ATP production. (C) Knockout and overexpression of MITOK and the percentage cellular viability of cell lines after treatment with either 25 or 30 µM of ZEA. (D) Cellular energy levels measured by ATPlite. (E) Cellular ROS levels measured by fluorescence microscopy. (F) The levels of protein synthesis were measured following treatment with ZEA for two days. (G) The percentage cellular viability of the four cell lines after treatment with various mycotoxins (ZEA, T-2 toxin, OTA, and DON) for 7 days. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n=3). p < 0.05 (*), p < 0.01 (**) and p < 0.001 (***), calculated by Student t-test.