Back to article: COX4-1 promotes mitochondrial supercomplex assembly and limits reactive oxide species production in radioresistant GBM
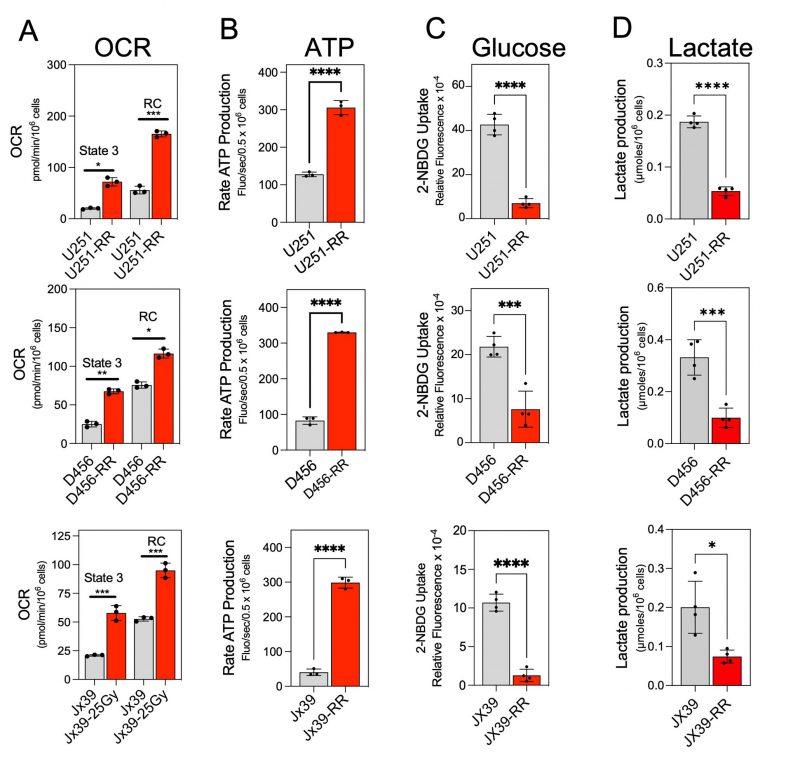
FIGURE 2: Acquired radioresistance in GBM cells is associated with a switch to an OXPHOS phenotype. (A) Quantification of the OCR in radiosensitive (U251, D456, and Jx39) and isogenic radioresistant (U251-RR, D456-RR, and Jx39-RR) cell lines after the addition of pyruvate/malate and ADP (state 3) and after the subsequent addition of FCCP (reserve capacity). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n=3). (B) Quantification of ATP production rate in radiosensitive and radioresistant cell lines, assessed by the reduction of NADP+ to NADPH. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n=3). (C) Quantification of cellular glucose uptake in the radiosensitive and radioresistant cell lines estimated with the non-phosphorylatable fluorescent glucose analogue 2-NBDG. Indicated cells were incubated with 100 μM 2-NBDG for 20 min, and 2-NBDG fluorescence was measured in a microplate fluorometer. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n= 4). (D) Quantification of extracellular lactate concentrations in cultures of the radiosensitive and radioresistant cell lines. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n= 4). OCR, oxygen consumption rate; Res capacity, reserve capacity; 2-NBDG, 2-(N-(7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl)amino)-2-deoxyglucose. p < 0.05 (*), p < 0.01 (**), p < 0.001 (***), and p < 0.0001 (****), calculated by Student t-test.