Back to article: Genotoxic stress signalling as a driver of macrophage diversity
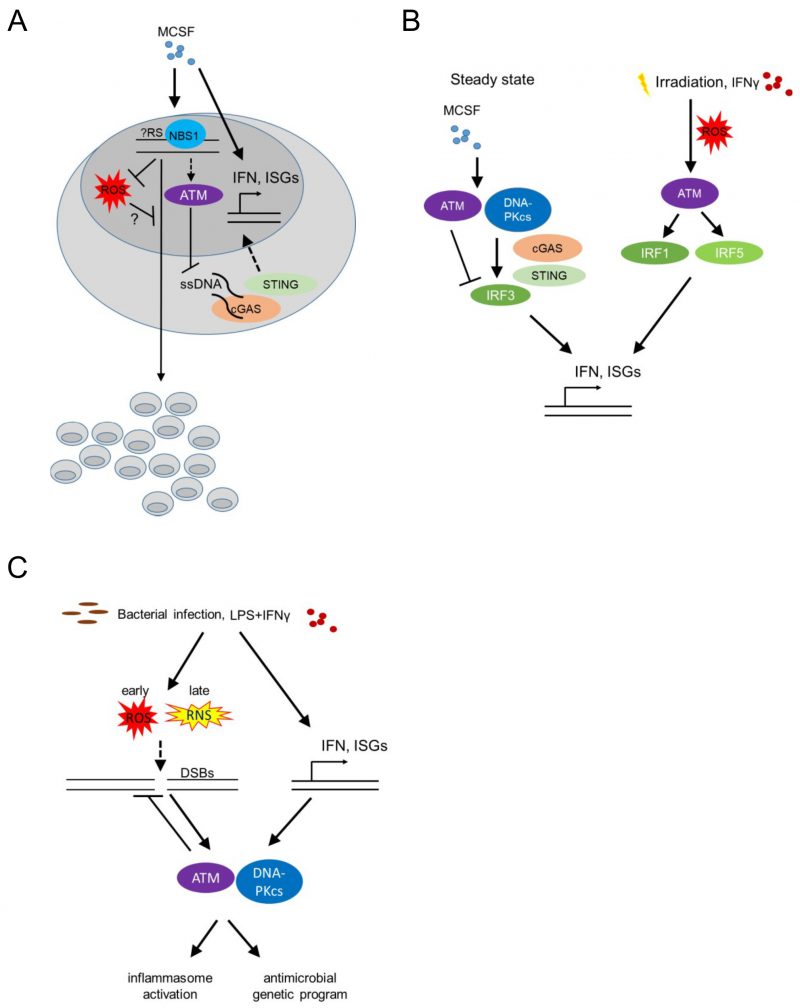
FIGURE 3: ATM regulates macrophage responses to MCSF, LPS and IFN-γ. (A) MCSF (macrophage colony stimulating factor) induces macrophage proliferation and differentiation, while activating type I interferon (IFN) responsive genes as well as potentially introducing genotoxic stress sensed by the MRE complex. This in turn downregulates ROS (reactive oxygen species) and activates downstream players of the DDR (such as ATM), thus suppressing genomic instability and promoting population expansion. Activated ATM in turn suppresses ssDNA accumulation in the cytoplasm and thus cGAS (Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase) – STING (Stimulator Of Interferon Response cGAMP Interactor)-induced IFNβ activation and interferon responsive genes. (B) At steady state MCSF upregulates type I IFN responsive genes by activating DNA-PK, STING and subsequently IRF3, while ATM itself suppresses the type I IFN response. Upon irradiation, increased expression of type I IFN responsive genes requires ATM-mediated IRF1 activation. Upon irradiation or following stimulation with IFNγ, ROS-induced ATM activation additionally leads to IRF5 upregulation, thus further activating type 1 IFN responses. (IRF-Interferon Regulatory Factor, ISG-Interferon Signature Genes). (C) Bacterial infection as well as stimulation with LPS and IFN-γ in BMDMs cause genotoxic stress, through the generation of ROS and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), thus activating ATM and DNA-PKcs in a type I IFN dependent manner. This leads to the upregulation of an antimicrobial macrophage genetic program as well as inflammasome activation.