Back to article: The role of lipids in autophagy and its implication in neurodegeneration
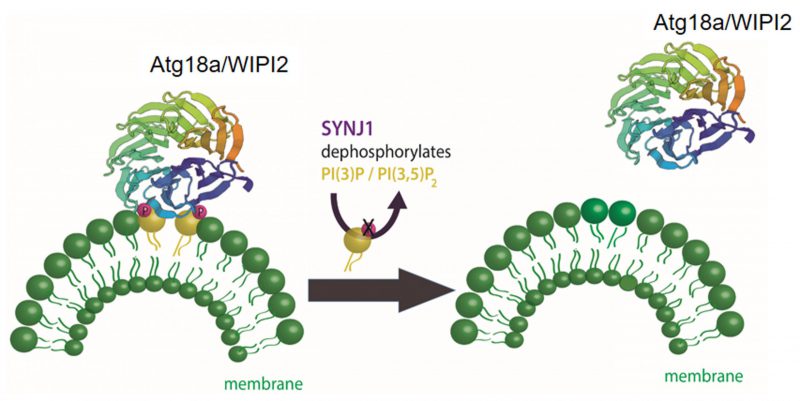
FIGURE 3: Maturation of autophagosomes relies on the turnover of PI3P/PI3,5P2 on autophagosomal membranes. In the initial phase of the autophagy pathway the accumulation of PI3P on the phagophore is required to recruit ATG18 and its mammalian homologue WIPI2. The WD40 domain in ATG18/WIPI2 folds into a seven bladed beta-propeller that contains two phenylalanine-arginine-arginine-glycine (FRRG) motifs in the sixth blade. This FRRG residue is a two sided recognition motif with binding specificity to PI3P/PI3,5P2. Maturation of nascent autophagosomes requires the shedding of autophagic factors like ATG18/WIPI2. At the presynaptic terminal, the phosphatase synaptojanin1 (Synj1) dephosphorylates PI3P/PI3,5P2 on autophagosomal membranes leading to the removal ATG18/WIPI2. Shedding of autophagic factors like ATG18/WIPI2 from the autophagosome is important for progression of the autophagic pathway.