Back to article: The role of lipids in autophagy and its implication in neurodegeneration
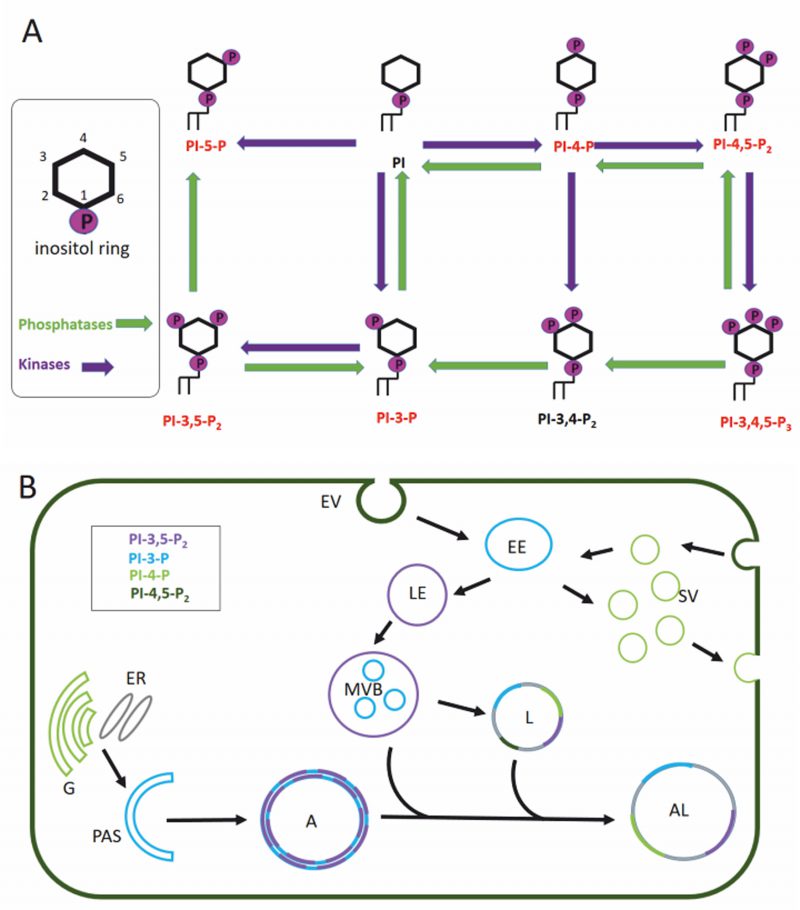
FIGURE 2: Phosphatidylinositol pathway and its role in cellular trafficking. (A) Phosphatidylinositols (PtdIns) are small lipids, consisting of two fatty acid chains, a glycerol backbone and an inositol ring. Kinases (violet) can phosphorylate the inositol ring at various positions (3, 4 and 5) leading to different phosphoinositides. We can differentiate between phosphatidylinositol monophosphates (PI3P, PI4P, and PI5P), diphosphates (PI3,4P2, PI3,5P2, PI4,5P2), and a triphosphate (PI3,4,5P3), that are substrates of different phosphatases (green) and kinases (see text for more details). Phosphoinositides that participate in the autophagy pathway are marked in red. (B) Membrane anchoring of the PtdIns is possible thanks to its glycerol backbone that positions the inositol ring towards the cytoplasmic site. Therefore, PtdIns often act as recognition motif for proteins containing a specific PI3P binding domain like pleckstrin homology (PH), FYVE, WD40 repeats, FERM, PTB, and PDZ to mediate signaling pathways including autophagy and clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Moreover, the specific enrichment of PtdIns can even mark the identity of intracellular organelles. Membranes are colored depending on postulated enrichment of specific phosphoinositols. PI4P enriched organelles are synaptic vesicles and Golgi, the phagophore and the early endosome are enriched in PI3P while the late endosome is enriched in PI3,5P2. The multivesicular body, a specialized late endosome, and the autophagosome are PI3,5P2 and PI3P positive organelles. Once the autophagosome fuses with the lysosome, the resulting autolysosome becomes enriched in PI3P, PI3,5P2 and PI4P. Golgi (G), endoplasmic reticulum (ER), phagophore assembly site (PAS), autophagosome (A), autolysosome (AL), multivesicular bodies (MVB), lysosome (L), endocytotic vesicle (EV), early endosome (EE), late endosome (LE), synaptic vesicle (SV).