Back to article: The role of lipids in autophagy and its implication in neurodegeneration
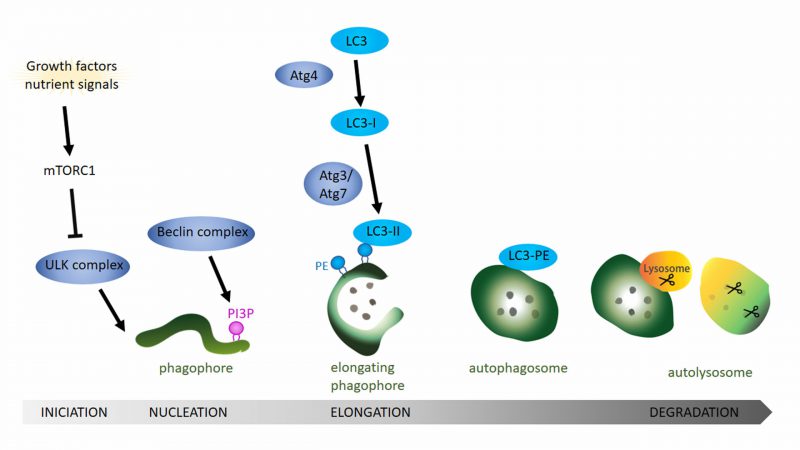
FIGURE 1: General overview of the autophagy pathway. Schematic drawing showing the autophagy process starting with the formation of the phagophore, followed by the completion of the autophagosome and finishing with the fusion of the autophagosome with the lysosome. Growth factors and nutrient signals inactivate the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTOR1) leading to the activation and recruitment of the ULK complex to the phagophore. Activity of the Beclin complex leads to local enrichment of phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PI3P). During the elongation of the phagophore, ATG4 processing of LC3 (ATG8 in Drosophila) and the subsequent conjugation to phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) on the phagophore membrane via ATG3 and ATG7 is essential step to form the autophagosome. After the fusion of the lysosome with the mature autophagosome, lysosomal proteases like cathepsin D degrade the autophagosomal content.