Back to article: Hyaluronan goes to great length
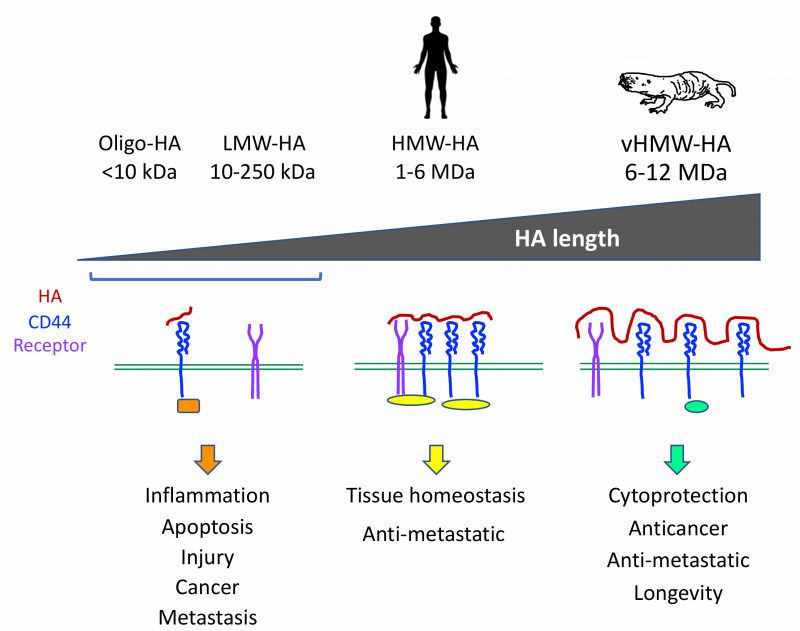
FIGURE 1: Biological effects of hyaluronans of different length. Hyaluronans of different length affect receptor interactions on cell surface and consequently engage different adaptor proteins (colored ovals and squares) on the cytoplasmic side activating distinct signaling pathways. Oligomeric hyaluronan (Oligo-HA) and low molecular weight hyaluronan (LMW-HA) do not cause clustering of CD44 (blue) and other receptors (purple). These hyaluronans are associated with inflammation, sites of injury, and promote cancer growth and metastasis. High molecular weight hyaluronan (HMW-HA) found in human tissues and in most other mammals, induces clustering of receptors and this signaling promotes tissue homeostasis, cell adhesion, and prevents metastasis by keeping cells in place. Very high molecular weight hyaluronan (vHMW-HA) is found in the naked mole rat. This hyaluronan shields CD44 receptor from interaction with other proteins leading to distinct downstream signaling characterized by cytoprotective effect, suppression of apoptosis. vHMW-HA has anticancer properties by limiting cell proliferation and metastasis and may ultimately promote longevity by protecting tissues from stress.