Back to article: The role of epigenetics in hypothalamic energy balance control: implications for obesity
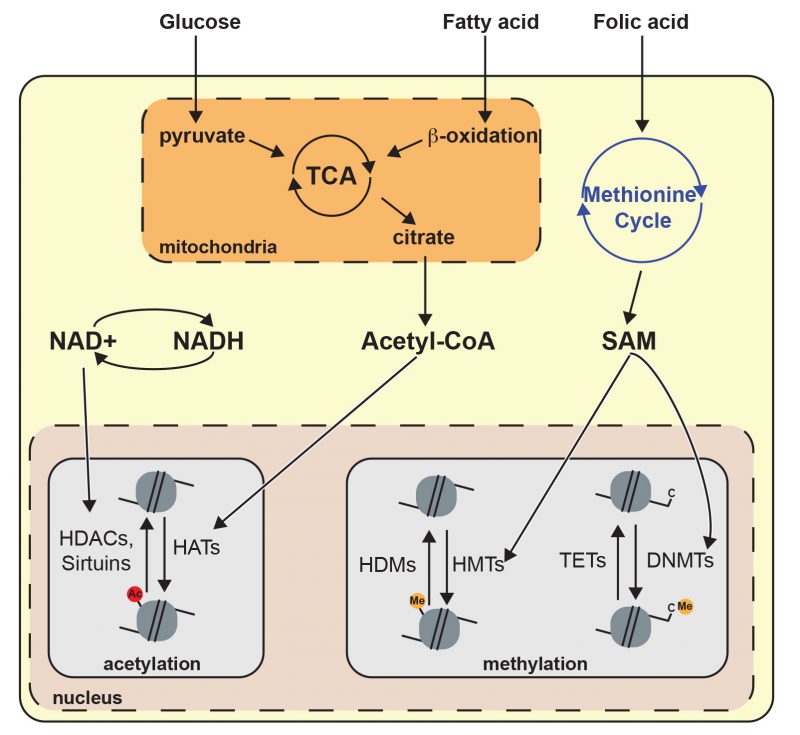
FIGURE 2: Metabolites influence chromatin architecture. Glucose and fatty acid catabolism produce acetyl-CoA through metabolic pathways including tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) and β-oxidation. Acetyl-CoA regulates histone acetylation because it is important for the enzymatic activity of histone acetyltransferases. NAD+ is produced by oxidative pathways and is a relevant cofactor for histone deacetylation mediated by sirtuins. The methionine cycle is the principal producer of S-adenosyl methionine (SAM), which is a cofactor for histone/DNA methyltransferase (HMT or DNMT). Histone deacetylase (HDAC), ten-eleven translocation (TET), histone demethylase (HDM).