Back to article: Hepatic stress associated with pathologies characterized by disturbed glucose production
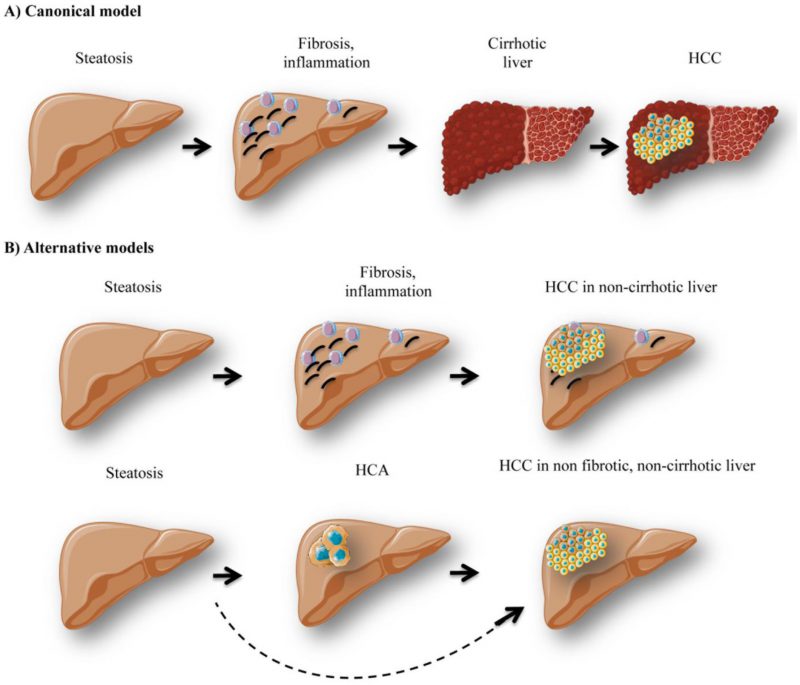
FIGURE 3: Different models of hepatocellular carcinoma development. The canonical model of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development (A) stipulates that patients with hepatic steatosis further develop inflammation / immune cell infiltration and fibrosis. Later on, excessive fibrosis and inflammation can lead to cirrhosis development and HCC. However, alternative models of hepatocarcinogenesis (B) have been observed in obese / GSDI patients. Indeed, steatotic patients, who do not present cirrhosis, can also develop HCC de novo, since fatty livers are favorable for carcinogenesis. Moreover, in GSDI patients, HCC can develop in non-fibrotic, non-cirrhotic liver. These tumors arise from the transformation of hepatocellular adenoma (HCA) to HCC.