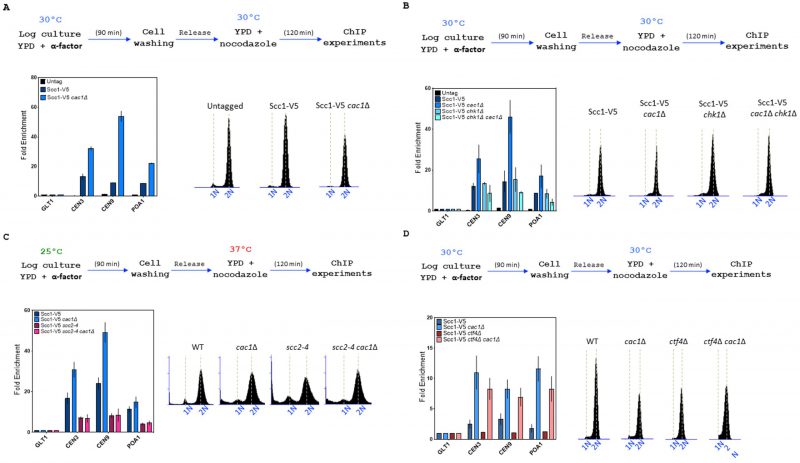
FIGURE 7: CAC1 inactivation increases cohesin level at chromatin in WT and ctf4Δ cells. Top, experimental design. In all experiments, DNA replication was monitored by FACS analysis of DNA content. (A) CAC1 inactivation increases cohesin level at centromere and chromosome arm. Cells of the indicated genotype were synchronized in G1 and were released into nocodazole imposed mitotic arrest for 120 minutes. Scc1 levels at two centromeres (CEN3 and CEN9), a chromosome arm cohesin binding site (POA1), and a negative control-binding site (GLT1) were measured by ChIP, followed by real-time qPCR. SEM shown represents four independent experiments. (B) The increased cohesin level at chromatin observed in absence of CAC1 is due to DNA damage. ChIP-qPCR analyses of Scc1 level at centromere and chromosome arm in WT, cac1Δ, chk1Δ, and chk1Δ cac1Δ. Same experimental conditions as in (A). (C) ChIP-qPCR analyses of Scc1 level at centromere and chromosome arm in WT, scc2-4, cac1Δ, and cac1Δ scc2-4. (D) CAC1 inactivation increases cohesin level at centromere and chromosome arm in absence of CTF4.