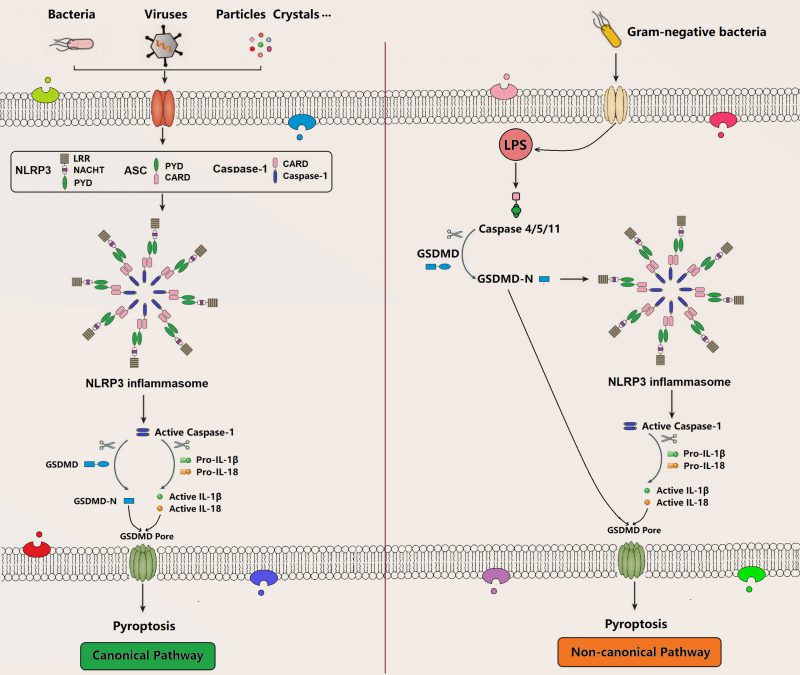
FIGURE 3. Canonical pathway and non-canonical pathway of pyroptosis. The canonical pathway is a caspase1-dependent pyroptosis pathway, and cells can activate inflammatory vesicles to trigger pyroptosis in response to multiple factors that causes caspase-1 activation. It can mature and secret pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-1β and IL-18 and simultaneously cleave GSDMD and oligomerize GSDMD-N-terminal fragment, which mediates the formation of membrane pores and subsequent pyroptosis. The non-canonical pathway is a caspase 4/5/11-dependent pyroptosis pathway that is activated by the Gram-negative bacterial cell wall fraction LPS, directly triggering pyroptosis through the cleavage of GSDMD. Meanwhile, the GSDMD-N-terminal fragment activates NLRP3 inflammasome to induce pyroptosis. NLRP3: NOD-like receptor protein 3; ASC: adaptor protein termed apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing an N-terminal pyrin domain (PYD) and a C-terminal caspase recruitment domain (CARD); GSDMD: gasdermin D; LPS: lipopolysaccharide.