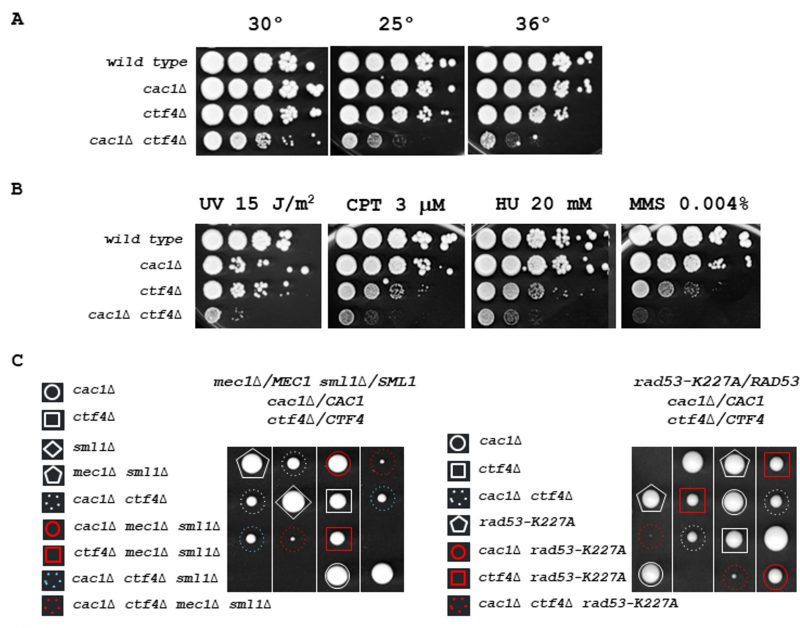
FIGURE 2: CAC1 is important for growth in the absence of CTF4. (A) cac1Δ ctf4Δ growth is affected at various temperatures. Tenfold serial dilutions of wild-type, cac1Δ, ctf4Δ, and cac1Δ ctf4Δ cells were spotted onto YPD plates and incubated at 30° (left), 25° (middle), or 36° (right) for 3 days. (B) cac1Δ ctf4Δ growth is affected in presence of DNA damage. Tenfold serial dilutions of wild-type, cac1Δ, ctf4Δ, and cac1Δ ctf4Δ cells were assayed on normal growth media (YPD), after UV irradiation or not, and on media containing the indicated DNA-damaging agents, camptothecin (CPT), hydroxyurea (HU), and methyl-methanesulfonate (MMS). (C) The S-phase checkpoint is required for cac1Δ ctf4Δ mutant viability. The diploid strains mec1Δ/MEC1 sml1Δ/SML1 cac1Δ/CAC1 ctf4Δ/CTF4 (left) and rad53-K227A/RAD53 cac1Δ/CAC1 ctf4Δ/CTF4 (right) were sporulated and one hundred tetrads were dissected on YPD plates and incubated at 30° for 5 days. Four representative tetrads are shown for each dissection. mec1Δ sml1Δ and rad53-K227A mutations are lethal in cac1Δ ctf4Δ cells.