Back to article: A pathological role of the Hsp40 protein Ydj1/DnaJA1 in models of Alzheimer’s disease
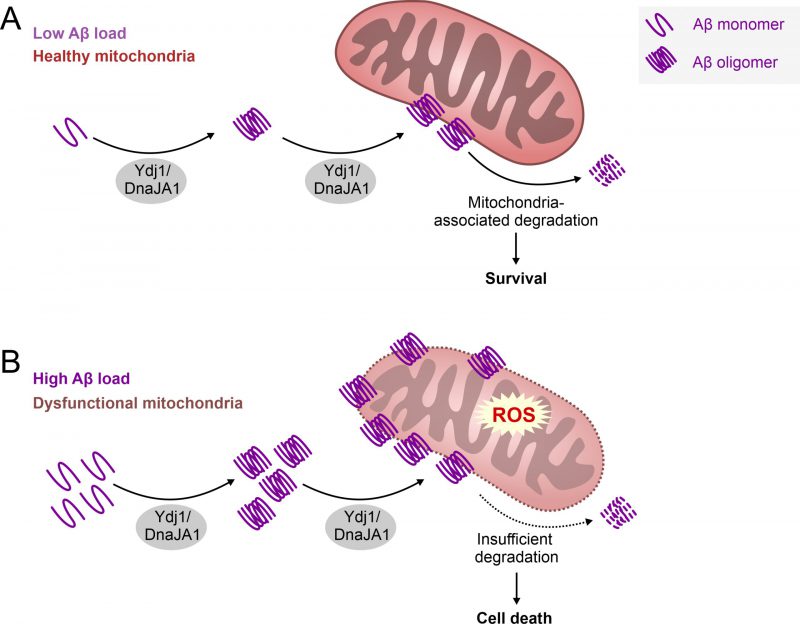
FIGURE 1: Hypothetical mechanism of Ydj1/DnaJA1’s role in Abeta toxicity. Abeta42 and its toxic oligomers are stabilized and translocated to mitochondria in a Ydj1/DnaJA1-dependent manner. We postulate that this behavior of Hsp40 family proteins is primed by the attempt to get rid of accumulating Abeta42 through mitochondria-dependent degradation (A). Nevertheless, in the case of high Abeta42 load or insufficient mitochondria-dependent degradation, Ydj1/DnaJA1 takes on a pathological role, leading to stressed mitochondria, eventually resulting in cell death promoting AD pathology (B).