Back to article:
RPA and Pif1 cooperate to remove G-rich structures at both leading and lagging strand
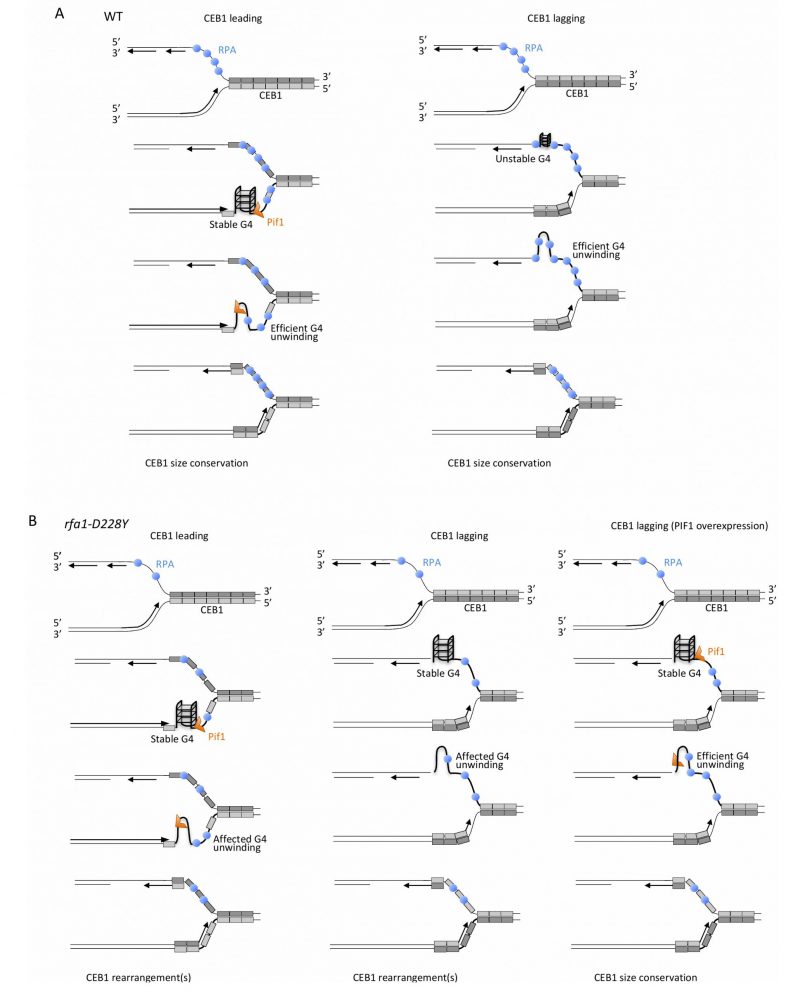
FIGURE 8: Mechanistic model for the unfolding of CEB1-G-rich structures by RPA and Pif1. (A) In WT cells, when the G-rich strand (light grey) is on leading strand (left part, CEB1 leading), stable G-quadruplexes structures are efficiently removed by Pif1, as proposed by Lopes and colleagues [33]. At the leading strand, RPA may cooperate with Pif1 either by preventing the refolding of the G4 structure or by recruiting Pif1 to the leading strand. When the G-rich strand (light grey) is replicated by the lagging polymerase (right part, CEB1 lagging) binding of RPA to the G-rich strand prevents formation of stable G-rich secondary structures. In this context, Pif1 is dispensable. (B) In the rfa1-D228Y mutant, at the leading strand (left part), the reduced affinity of RPA for G-rich ssDNA either reduce the ability of RPA to prevent the refolding of the G4 structure or decrease Pif1 recruitment. The decrease in RPA affects G4-unwinding and leads to the formation of CEB1 rearrangements. At the lagging strand (middle part), the decrease affinity of RPA for G-rich ssDNA facilitates the formation of stable G-rich structures, affects their unwinding, and generates CEB1 instability. In such a case, overexpression of Pif1 (right part) can efficiently unwind G-rich structures, leading to CEB1 size conservation.
33. Lopes J, Piazza A, Bermejo R, Kriegsman B, Colosio A, Teulade-Fichou M-P, Foiani M and Nicolas A (2011). G-quadruplex-induced instability during leading-strand replication. Embo J 30(19): 4033–4046. 10.1038/emboj.2011.316

