Back to article: MiR-200c reprograms fibroblasts to recapitulate the phenotype of CAFs in breast cancer progression
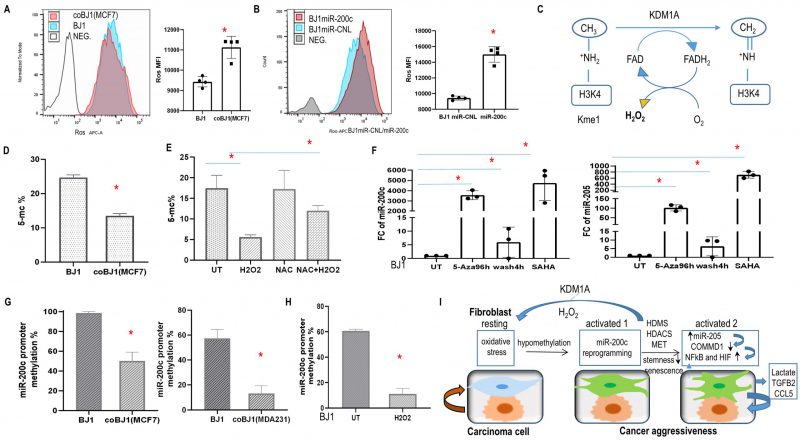
FIGURE 10: Oxidative stress, epigenetic modification regulated miR-200c expression and model of fibroblasts and carcinoma cells cross talk modulated by miR-200c via ROS. (A) ROS level in BJ1 cells under homotypic and coculture condition. *p<0.05. (B) ROS level in BJ1miR-200c or control. (C) Histone demethylation mediated by KDM1A demethylase through an FAD-dependent amine oxidase reaction, releasing one molecule of H202. (D, E) Global DNA methylation was measured by 5-mC percentage in sorted co-culture and homotypic BJ1 cells or with redox modulators. (F) Fold change of miR-200c and miR-205 in BJ1 fibroblasts exposed to drugs regulating the epigenetic repressive state. (G, H) Promoter DNA methylation of miR-200c in fibroblasts. BJ1 cells under homotypic or co-culture condition or exposure to H2O2 for 4 days. *p<0.05. (I) Model of fibroblasts and carcinoma cells cross talk regulated by miR-200c. In the TME, ROS causes DNA hypomethylation of fibroblasts, which promotes miR-200c transcription. Reprogramming fibroblasts via miR-200c towards MET/senescence reduces stemness, induces aberrant chromatin changes and histone demethylation mediated by KDM1A demethylase through an FAD-dependent amine oxidase reaction with H202 release. Meanwhile it induces miR-205 and reduces COMMD1 expression along with NFκB and HIF activation. Furthermore, these reprogrammed fibroblasts promote cancer aggressiveness.