Back to article: Therapeutic potential of HDAC6 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
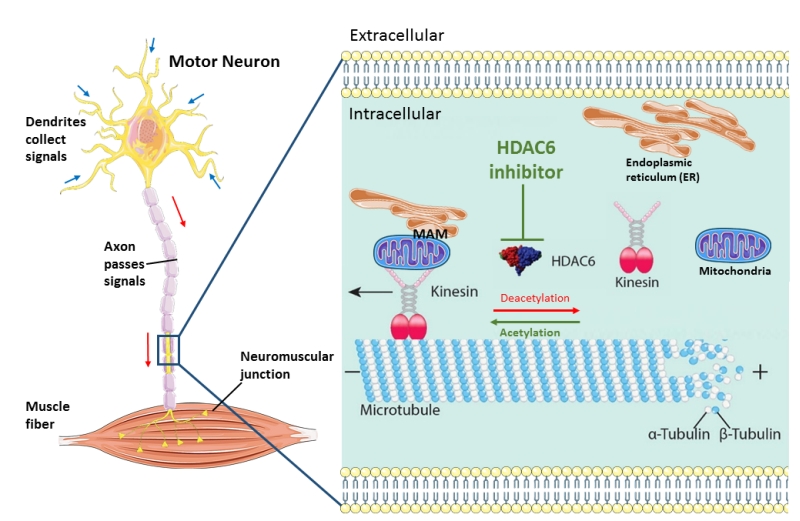
FIGURE 1: Schematic overview of the machinery of HDAC6 inhibition in rescuing axonal transport defects in ALS. Axonal transport cargoes, such as ER and mitochondria, anchored to the motor protein kinesin. The molecular motors kinesin travel along the microtubules with their bound cargoes in an anterograde direction. HDAC6 is an important regulator of axonal transport by regulating the acetylation state of α-tubulins which build up microtubules with β-tubulins. In stabilized microtubules, the minus end facing the soma and dynamic plus end facing the synaptic terminals. Under cell stress, the motor neuron start ‘dying back’ from the distal part of axon caused by insufficient metabolic supply. HDAC6 inhibition increase the acetylation level of microtubules and increase the localization of MAMs along microtubules and finally speed up axonal transport of ER and mitochondria. (This image is constructed based on the images from Servier Medical Art (http://smart.servier.com/) and Neurobiol Dis. 2017 Sep; 105:300-320.doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2017.02.009).