Back to article: VDAC1 at the crossroads of cell metabolism, apoptosis and cell stress
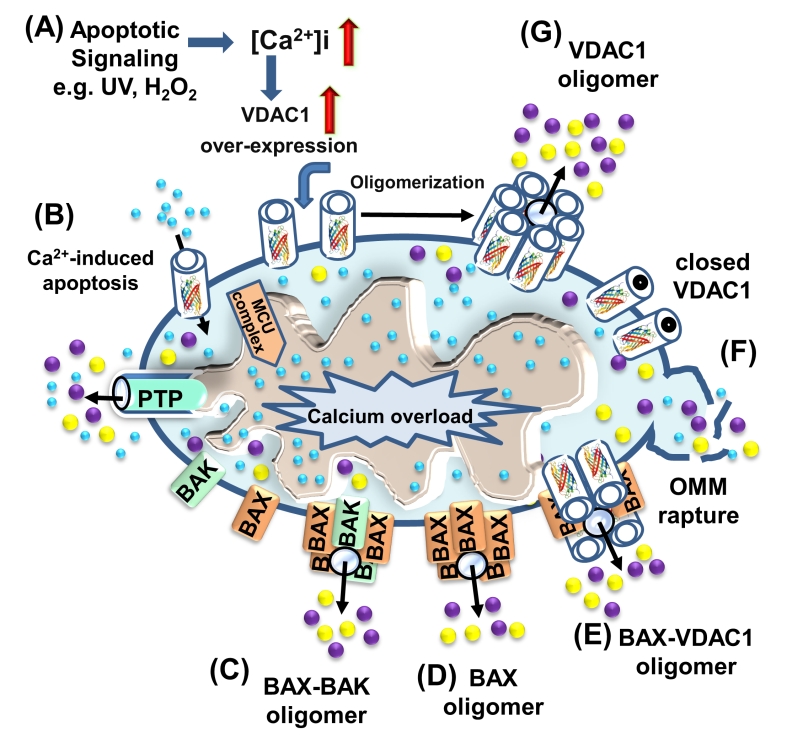
FIGURE 5: VDAC1 function in cell death, with apoptosis inducers enhancing VDAC1 expression levels and oligomerization. A schematic representation of VDAC1 function in cell death – Different models for the release of apoptogenic proteins, such as Cyto c (purple) and AIF (yellow), are shown. (A) Proposed model suggesting that apoptotic stimuli or conditions cause enhanced VDAC1 expression via increases in [Ca2+]i levels or transcription factors, leading to activation of the VDAC1 promoter. The increase in VDAC1 expression shifts the equilibrium towards the VDAC1 oligomeric state, forming a hydrophilic protein-conducting channel capable of mediating the release of apoptogenic proteins (e.g., Cyto c and AIF) from the mitochondrial IMS to the cytosol. (B) Mitochondrial Ca2+ overload induces apoptosis. Ca2+ transport across the OMM, as mediated by VDAC1, and then across the IMM, as mediated by the MCU, leads to Ca2+ overload in the matrix. This, in turn, causes dissipation of the membrane potential, mitochondrial swelling, PTP opening, Cyto c/AIF release and the triggering of apoptotic cell death. (C) Bax/Bak oligomerization and activation, forming a route for Cyto c/AIF release. (D) Bax activation leads to its association with the OMM, followed by its oligomerization as a large oligomer/complex, forming a Cyto c/AIF-conducting channel. (E) The interaction of the pro-apoptotic protein Bax with VDAC1 forms hetro-oligomers that mediate Cyto c/AIF release. (F) Prolonged VDAC1 closure leads to mitochondrial matrix swelling and OMM rupture, resulting in the appearance of a non-specific release pathway for apoptogenic proteins.