Back to article: VDAC1 at the crossroads of cell metabolism, apoptosis and cell stress
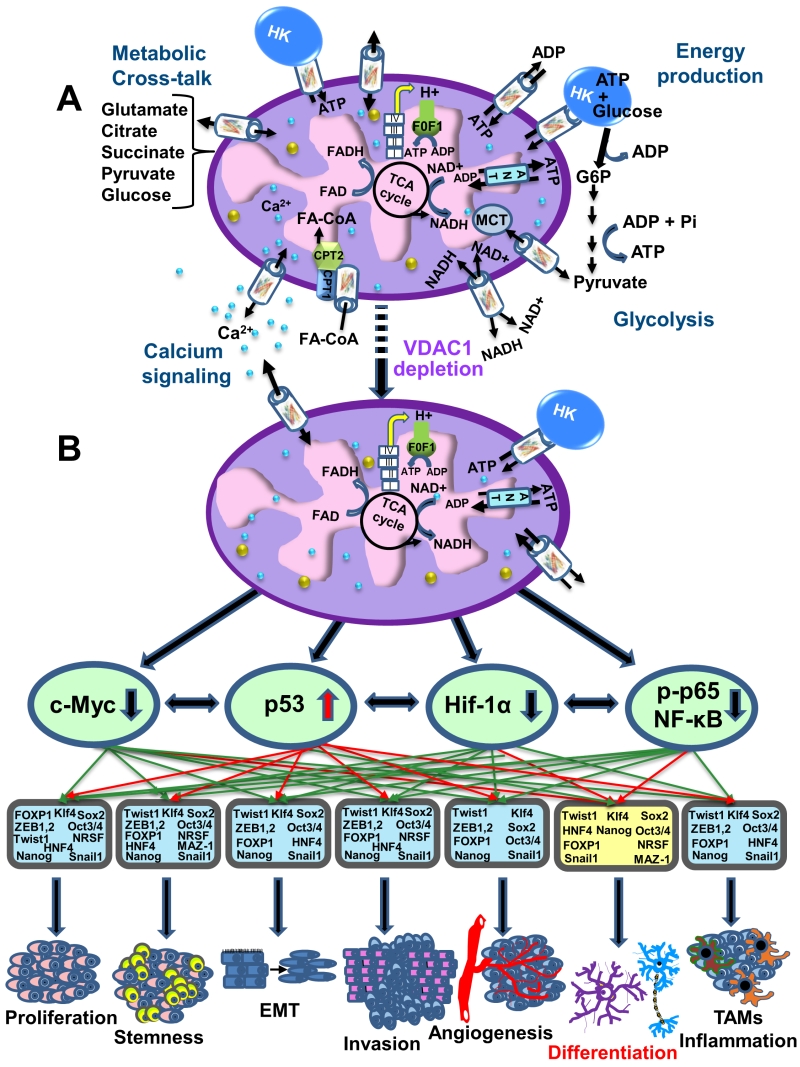
FIGURE 4: VDAC1-depletion and metabolic reprogramming leading to alterations in key transcription factor levels and biological processes: a reversal of oncogenic properties and cell differentiation. (A) A schematic presentation of mitochondria in a cancer cell before treatment with hVDAC1 siRNA. Here, cancer cells maintain homeostatic energy and metabolic states, with HK bound to VDAC1 accelerating glycolysis and mitochondrial function to allow sufficient ATP and metabolite precursor levels to support cell growth and survival. (B) VDAC1 depletion leads to dramatic decreases in energy and metabolite generation. This leads to changes in master metabolism regulator (p53, HIF1-α, c-Myc and NF-kb, P65) expression levels, which alters the expression of transcription factors associated with stemness, EMT, cell proliferation, invasion, TAMs and angiogenesis, while leading to differentiation into astrocyte- or neuron-like cells.