Back to article: VDAC1 at the crossroads of cell metabolism, apoptosis and cell stress
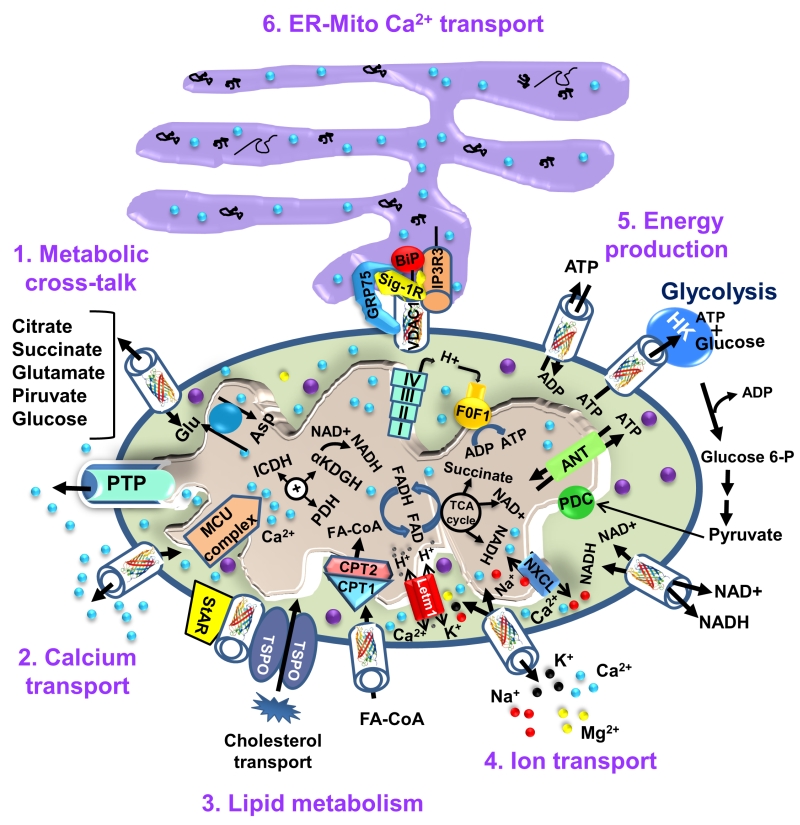
FIGURE 2: VDAC1 as a multi-functional channel involved in metabolite, cholesterol and Ca2+ transport, energy production and in ER-mitochondria structural and functional association. The functions of VDAC1 in cell life include control of the metabolic cross-talk between the mitochondria and the rest of the cell energy production, regulation of glycolysis via binding of HK, Ca2+ signaling and cholesterol transport. The various functions of VDAC1 in the cell and mitochondria functions are presented. These include: 1. Control of the metabolic cross-talk between mitochondria and the rest of the cell; 2. Transport of Ca2+ to and from the IMS and acting in Ca2+ signaling; 3. Lipid metabolism; 4. Transport of ions, such as Mg2+, Zn+, Na+ and K+; 5. Mediating cellular energy production by transporting ATP/ADP and NAD+/NADH and acyl-CoA (FA-CoA) from the cytosol to and from the IMS, and regulating glycolysis via association with HK; 6. Structurally and functionally contributing to ER-mitochondria contacts, mediating Ca2+ transport from the ER to mitochondria. Ca2+ influx and efflux systems in the IMM are shown. The mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter (MCU), in association with a calcium-sensing accessory subunit (MCU1), mediates Ca2+ transport from the IMS into the matrix. The ryanodine receptor (RyR) in the IMM mediates Ca2+ influx. NCLX, a Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, mediates Ca2+ efflux from the matrix to the IMS. High levels of matrix Ca2+ trigger the opening of the PTP, a fast Ca2+ release channel. Molecular fluxes are indicated by arrows. The function of Ca2+ in regulating energy production is mediated via activation of the TCA cycle enzymes pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), isocitrate dehydrogenase (ICDH) and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (α-KGDH), leading to enhanced activity of the TCA cycle. The electron transport chain (ETC) and the ATP synthase (FoF1) are also presented. VDAC1 mediates the transfer of acyl-CoAs across the OMM to the IMS, where they are converted into acylcarnitine by CPT1a for further processing by β-oxidation. VDAC1 is involved in cholesterol transport by being a constituent of a multi-protein complex, the transduceosome, containing StAR/TSPO/VDAC1.The ER-mitochondria association is presented with key proteins indicated. These include the inositol 3 phosphate receptor type 3 (IP3R3), the sigma 1 receptor (Sig1R) (a reticular chaperone), binding immunoglobulin protein (BiP), the ER HSP70 chaperone, and glucose-regulated protein 75 (GRP75). IP3 activates IP3R in the ER to release Ca2+ that is directly transferred to the mitochondria via VDAC1.