Back to article: The long non-coding RNA H19 suppresses carcinogenesis and chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma
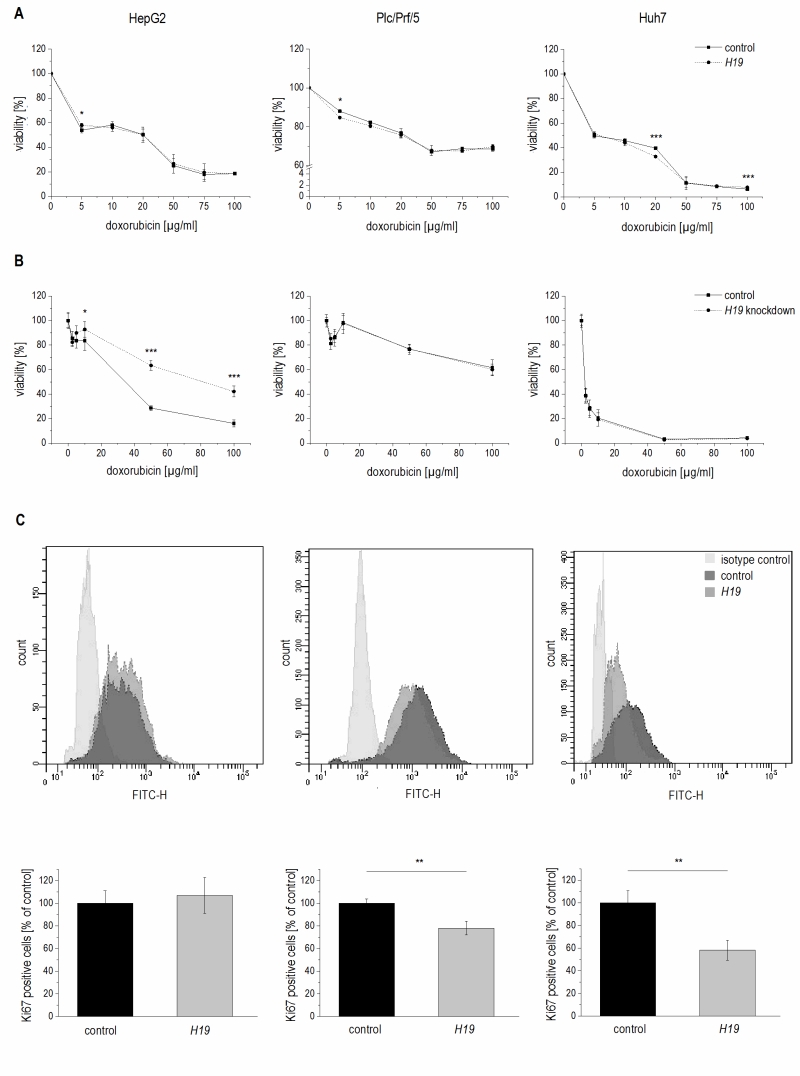
FIGURE 5: Effect of H19 overexpression and knockdown on cell viability and proliferation in HepG2 (left panels), Plc/Prf/5 (middle panels), and Huh7 (right panels) cells. (A) Cytotoxicity assay with doxorubicin in stably H19 overexpressing (H19) or vector control (control) cells normalized to their respective untreated control (n=2, sextuplicates). (B) Cytotoxicity assay with doxorubicin after transfection with H19 gapmer (H19 knockdown) and control gapmer (control) normalized to their respective untreated control (n=2, sextuplicates). (C) FACS analysis of the proliferation marker Ki67 in stably H19 overexpressing (H19) and vector control cells (control). Representative histograms of Ki67 FACS analysis are shown (upper panels). Quantification of Ki67 positive cells expressed as percent of control (n≥2, triplicates). The p values were calculated by two-sample t-test or Mann-Whitney U test depending on the data distribution. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.